INTRODUCTION
Congenital heart diseases (CHDs) are abnormalities within the cardiocirculatory structure or operate due to abnormal heart development throughout foetal life
CHDs are classified into:
- Cyanotic CHDs (cause blue discoloration due to relative lack of oxygen)
- Acyanotic CHDs
The diagnosing of congenital heart disease (CHD) encompasses varied anatomical abnormalities of the center and therefore the great arteries.
Modern treatment ways are primarily directed towards the surgical repair of those structural defects.
These treatment approaches are significantly life prolonging however principally not curative, leading to life-long uninterrupted vessel residua and sequels, e.g., residual shunts, valvular lesions, or implantation of prosthetic materials inflicting an inherent risk for infective endocarditis in these patients.
Infective endocarditis could be a probably fatal event that, upon manifestation, causes a awfully high morbidity and mortality.
In samples of the overall population regarding 50% of patients with infective carditis want surgical interventions for therapy and therefore the mortality reaches 30% at one year.
The manifestation of infective carditis in patients with congenital heart disease appears to elevate the chance for a fatal outcome at intervals the primary year following diagnosing over 30-fold as compared to congenital heart disease patients without infective endocarditis .
Oral manifestations recorded for patients with CHD were cyanosis, pale tissues and cleft palate and lip.
Other clinical findings related to CHD embrace delayed teeth eruption, teeth hypoplasia and high decay incidence.
The ultrastructure and composition of healthy enamel and dentin account for his or her ability to resist the consequences of cariogenic bacterium and alternative damaging factors within the oral atmosphere.
Literature review reportable that CHD could result in changes concerning oral health
Figure - 1
TYPES OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
- Transposition of the great arteries
- Pulmonary valve stenosis
- Single ventricle defects
- Hypoplastic heart syndrome
- Coarctation of aorta
- Atrial septal defect
- Aortic valve stenosis
- Patent ductus arteriosus
- Pulmonary atresia
- Ventricular septal defect
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Atrioventricular septal defect
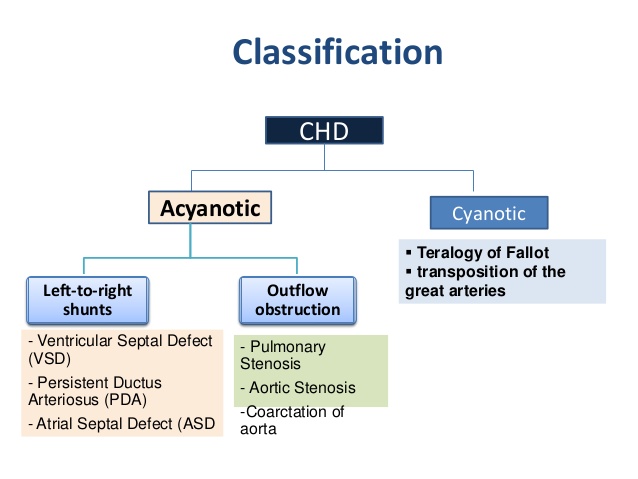
Photo credit: www.slideshare.net
EFFECT OF CHD IN ENAMEL
Enamel contains a protecting role on the tooth; loss of enamel exposes the sensitive dentin underneath.
Once damaged, enamel is mostly unable to recover.
The presence of alterations in enamel and dentin of deciduous incisors obtained from CHD patients.
These changes were discovered within the ultrastructure moreover because the mineral content (Ca and P) of enamel and dentin.
Al-Etbi and Al-Alousi results discovered that kids with ventricular congenital heart defect (acyanotic CHD) had a high share of enamel defects.
ESEM analysis of enamel showed a rise in dissolution once preparation by etching.
ESEM analysis for dentin of acyanotic specimens showed increase in lateral branching of dentinal tubules.
Widening of dentinal tubules was evident. additionally, thinning of peritubular dentin was discovered.
EFFECT OF CHD IN DENTAL CARIES
Dental caries is primarily considered as an communicable disease caused by the establishment of the tooth surface by a infective microorganism biofilm. A shift of the biofilm from a state being compatible with health to an acidic environment favors the proliferation and possibly phenotypic adaption of acid tolerant bacterium ultimately amplifying the acidic potential of the biofilm. Mainly
Streptococcus sp., namely
- Streptococcus mutans, have been advised to be answerable for the acidification of the biofilm.
More recent etiologic models take into account that several alternative endogenous bacterium that are gift among the dental biofilm may also contribute to the acidification whereas alternative species are capable of base formation and so to counteract acidification.
The formation of a dental biofilm is an important step for the formation of decay however it's normally accepted that dental caries features a advanced complex etiology and needs the interactions between varied impacts, i.e., the biofilm, salivary functions, the tooth structure, totally different genetic and behavioral factors.
The latter specifically refers to the diet and also the oral hygiene efforts of the patient.
The frequent activity of fermentable carbohydrates, i.e., sugars, will induce a chronic acidification of the mature biofilm.
Due to an intense production of principally weak organic acids the pH drops below a essential worth leading to decomposition of the hydroxyapatite that includes the mineral section of the tooth.
Upon progression the demineralization leads to the collapse of the tooth surface and leads to the manifestation of a clinically detectable decay lesion, together with discoloration and cavitation.
Photo credit: https://www.woodbridgekids.com
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AND ORAL CAVITY
Infective endocarditis needs bacteremia with microorganisms that may with success adhere to the endocardial surfaces
The individual status for the manifestation of infective carditis is powerfully influenced by the presence and severity of oral diseases.
The oral cavity is taken into account a extremely relevant supply for bacteriemia resulting in infective endocarditis.
Bacteremia derived from the oral cavity is detectable once minor tissue layer trauma, together with not solely varied standard dental diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, however additionally frequent daily activities, i.e., teeth brushing or mastication.
Elevated risk of manifestation of infective endocarditis, there exists some proof that young patients with CHD show increasing amounts of dental deposits, i.e., plaque, additional plaque evoked gingival inflammation, lower compliance with dental maintenance care, and poorer routine oral hygiene measures throughout childhood and adolescence.
Antibiotic prophylaxis has been counseled to handle the elevated risk for infective carditis throughout occasional diagnostic and therapeutic dental procedures in patients with vessel anomalies, together with people with CHD.
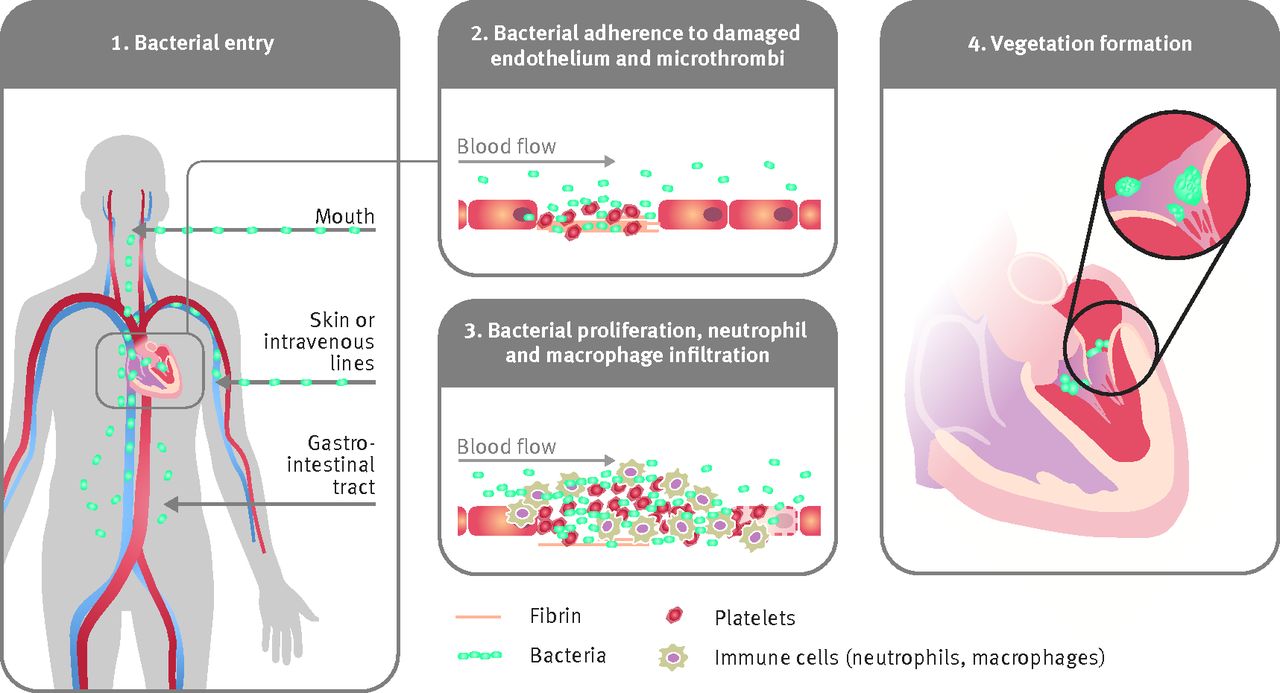
Photo credit: https://www.bmj.com
EFFECT OF CHD WITH PERIODONTITIS
Periodontitis may be a biofilm-associated chronic inflammatory disease poignant the tooth supporting periodontal tissue at the animal tissue margin resulting in the destruction of the periodontal ligament and also the alveolar bone.
Periodontal diseases are evaluated by completely different ways.
The gingival bleeding index was utilized in this study as a tool for kids periodontitis analysis.
As a result the tissue loss causes associate increasing depth of the gingival sulcus thereby remodeling into a periodontal pocket, the loosening of the tooth and eventually the loss of the whole tooth.
Immune-inflammatory host response has been introduced because the main cause of periodontal disease.
The factors that activate the pathway of arachidonic metabolism are presently called the most cause of periodontitis except pathogenic microorganisms.
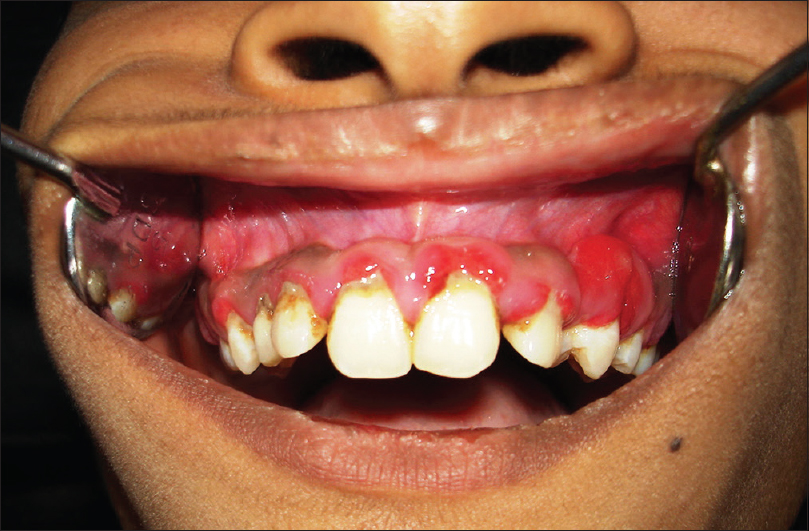
Photo credit: http://www.jdas.in
EFFECT OF CHD IN PERIAPICAL PERIODONTITIS.
Progressing caries finally reaches the pulp chamber and causes necrosis of the pulp tissue, ultimately leading to microorganism infection and inflammation of the periapical tissue.
Root canal treatment is that the ordinarily accepted therapeutic approach to deal with each entities.
patients with CHD presented with considerably higher amounts of plaque compared to wholesome controls herein.
This may cause the idea of poorer compliance with oral hygiene measures.
Despite no clear evidence, teeth showing periapical disease are advised to cause transient bacteriemia in remote sites of the organism.
Herein, heart healthy subjects presented a better average range of teeth with periapical disease than patients with CHD. However, this distinction between the teams was important in female subjects solely.
One may speculate that female patients with CHD adhere higher to oral validating care and are a lot of rigorous in maintaining oral health than male patients.
Since periapical periodontal disease could be a consequence of progressing cavity, again, these knowledge appear to additional support the conclusion that patients with CHD have a lower dental caries expertise than healthy controls.
Based on radiographic knowledge, periodontal bone loss at each single stock-still and multi rooted teeth was 3 times as high in heart healthy people compared to subjects with CHD.
Highly important supply of entry for bacterium incursive the systemic blood.
The extent appears to correlate with the progression of periodontal disease due to the deepening of the periodontal pockets.
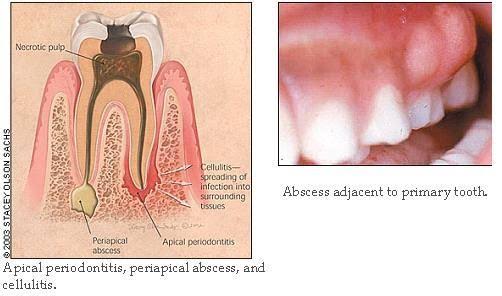
Photo credit: https://www.ida.org.in
DENTAL CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHD PATIENTS
As for all patients presenting to the clinician in primary dental care, the primary step in providing acceptable care is to get and document a comprehensive medical and social history.
Preventive dentistry within the type of dietary recommendation, home and workplace fluoride therapy, and oral hygiene recommendation can and may be provided for all patients.
Fissure sealant placement might or may not be acceptable, depending on age and cooperation, however ought to be considered as before long because it is possible.
Placement of resin-modified or conventional glass-ionomer sealants could also be thought of interim measure for teeth particularly in danger of dental caries that aren't nonetheless totally erupted, or for children who are unable to tolerate the position of a standard resin sealant.
An INR(International normalized ratio) ought to be obtained at intervals twenty four hours of the projected surgery.
Because excessive hurt could also be seen in a little variety of kids with polycythaemia because of cyanotic CHD, a full blood count and coagulation screen might be prudent for this group before
surgical medical care.
Appropriate consultation with the cardiac and anaesthetic groups at the planning stage forms the premise for minimize the risks throughout sedation and general anesthesia.
Treatment of dental caries, whether or not surgical or restorative,must be provided within the context of the risk of IE.
Orthodontic treatment, as well as the placement of area maintainers, can be provided for children with CHD, but only with the strictest observation and maintenance of excellent oral hygiene to reduce the risks of developing IE
Primary aid suppliers ought to be adept at the placement of Stainless-steel crowns, and may think about their use for children with CHD who present with dental caries.

Photo credit: https://expressionsfamilydental.com
CONCLUSION
Pediatric patients with CHD expertise insignificantly higher dental decay, disease, and saliva Lactobacilli colony counts.
The frequency of decayed tooth and gingival diseases in healthy kids is high, and hence, additional tending attention in our health system is required for healthy kids.
Several disease-related factors could also be concerned in manufacturing these changes; these include
- hemodynamic alterations
- malnutrition
- infective endocarditis
- medication
- hypoxia
Cooperation between pediatric cardiologists and pediatric dentists ought to be enlarged.
Spreading awareness of dental health and cavity risk among CHD kids and their parents should become a priority.
More efforts for cavity interference should be directed towards CHD children, particularly those in developing countries as they're at higher risk.
REFERENCE








0 Comments